Brain imaging research is a fundamental area of modern neuroscience that allows scientists and doctors to study the human brain without surgery or invasive procedures. By using advanced imaging technologies, researchers can see the brain’s structure, activity, chemistry, and connections in living people, helping explain how the brain works in health and disease.
What Is Brain Imaging Research?
Brain imaging research involves the use of medical and scientific tools to create visual representations of the brain. These images help researchers understand how different regions of the brain are organized, how they communicate, and how they change over time.
Unlike earlier approaches that relied on animal studies or post-mortem examinations, brain imaging allows real-time observation of the human brain while a person is thinking, moving, or resting. This has dramatically expanded our understanding of cognition, behavior, and neurological disorders.
Main Types of Brain Imaging Techniques
Structural Brain Imaging
Structural imaging focuses on the physical anatomy of the brain.
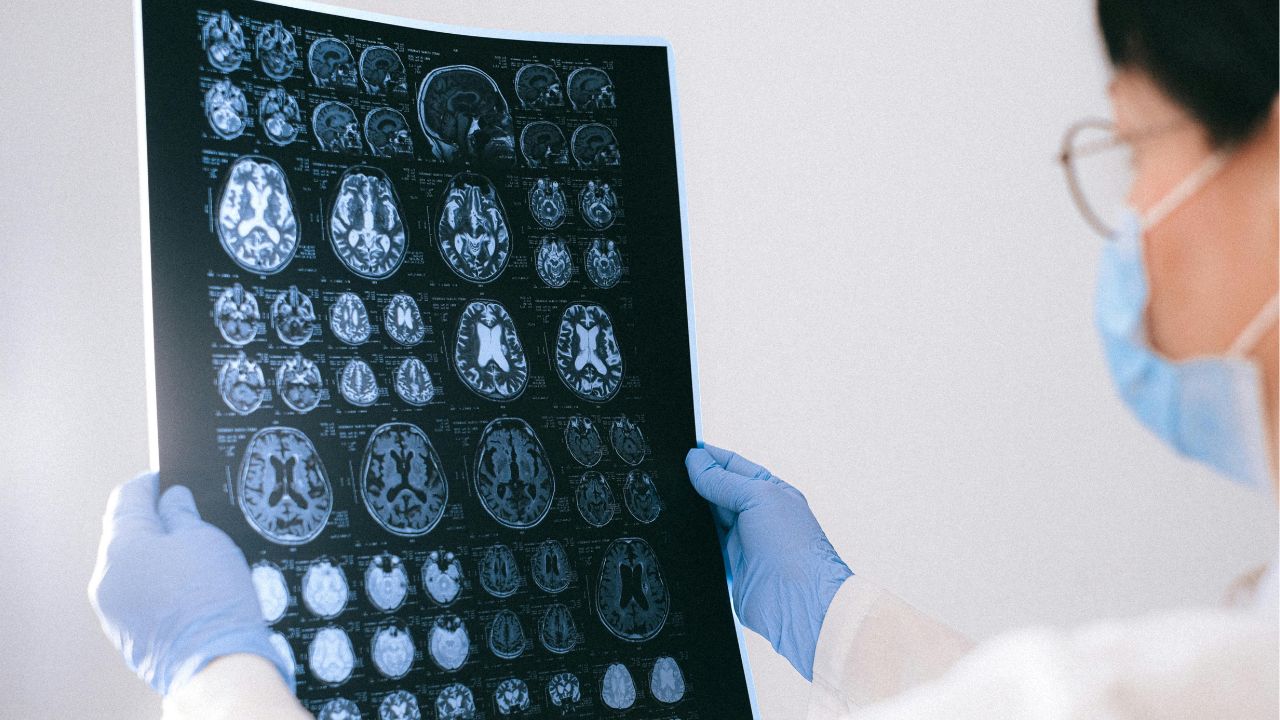
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Produces detailed images of brain tissue, commonly used to detect tumors, strokes, brain atrophy, and developmental abnormalities.
- CT (Computed Tomography): Uses X-rays to quickly identify bleeding, fractures, or major structural damage, often in emergency settings.
Functional Brain Imaging
Functional imaging shows how the brain works rather than how it looks.
- fMRI (Functional MRI): Measures changes in blood flow related to neural activity, widely used in research on memory, attention, emotions, and decision-making.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography): Tracks metabolic activity and neurotransmitter systems using safe radioactive tracers.
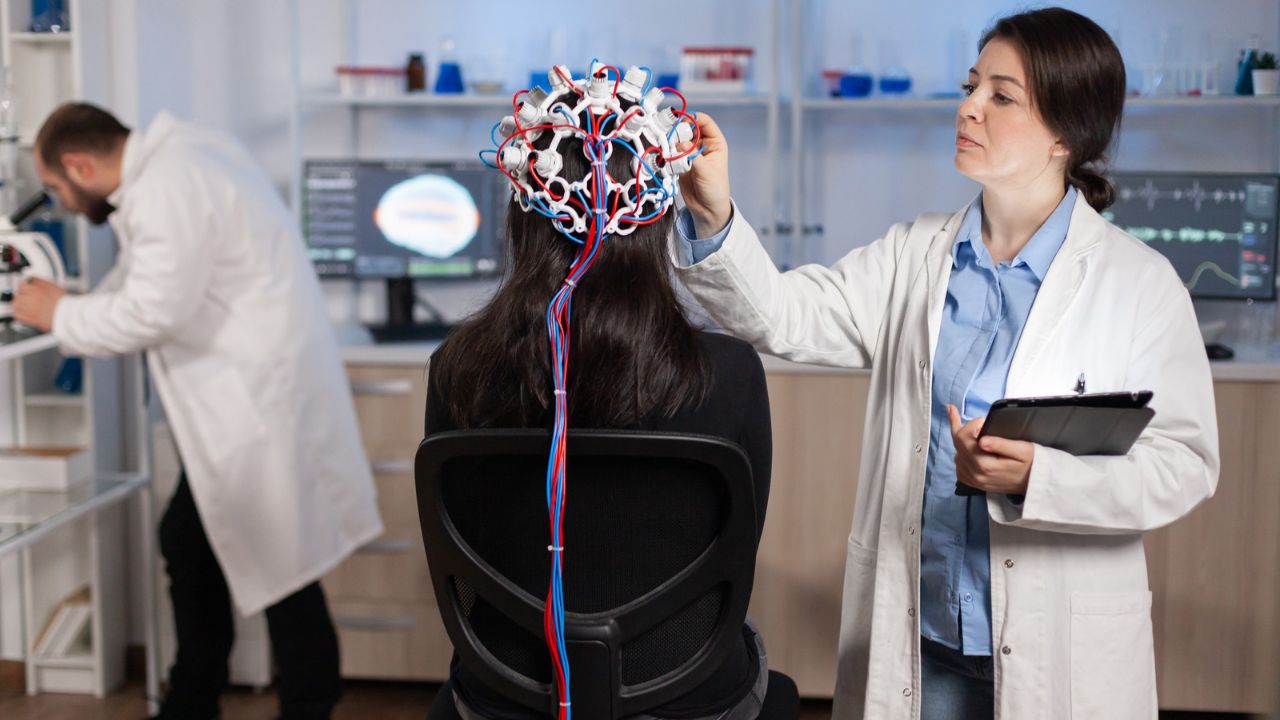
- EEG (Electroencephalography): Records electrical signals from the brain, offering precise timing of brain activity.
- MEG (Magnetoencephalography): Measures magnetic fields generated by neurons, combining high temporal accuracy with better spatial detail than EEG.
Connectivity and Advanced Imaging
- DTI (Diffusion Tensor Imaging): Maps white-matter pathways, showing how different brain regions are connected.
- Resting-state fMRI: Examines brain networks when a person is not performing a task, revealing core functional systems.
Why Brain Imaging Research Matters
1. Understanding How the Brain Works
Brain imaging helps link mental processes such as memory, language, emotion, and attention to specific brain regions and networks. This has been essential for building modern theories of cognition and behavior.
2. Improving Diagnosis of Brain Disorders
Imaging tools are critical in diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, stroke, traumatic brain injury, and brain tumors. In mental health, imaging is helping identify biological patterns linked to depression, schizophrenia, and anxiety disorders.
3. Guiding Treatment and Medical Decisions
Doctors use brain imaging to plan surgeries, monitor recovery after injury, evaluate treatment effectiveness, and personalize care. In some cases, imaging helps predict which treatments are most likely to work for individual patients.
4. Advancing Mental Health Research
Brain imaging supports the understanding of psychiatric disorders as brain-based conditions rather than personal weaknesses. This shift has reduced stigma and improved scientific approaches to mental health care.
5. Driving Technological Innovation
Brain imaging data is essential for the development of brain–computer interfaces
FAQs:
What is brain imaging research in simple terms?
Brain imaging research is the study of the brain using advanced technologies that create pictures or maps of brain structure and activity. It helps scientists see how the brain works in real time without surgery.
What are the most common brain imaging techniques?
The most common techniques include MRI, fMRI, CT scans, PET scans, EEG, and MEG. Each method provides different information about brain structure, function, or electrical activity.
How is brain imaging used in medicine?
Doctors use brain imaging to diagnose and monitor conditions such as stroke, brain tumors, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic brain injuries. It also helps guide treatment decisions and surgical planning.